Introduction
Compass surveying is a vital technique in the field of land surveying, known for its simplicity and effectiveness. Yet, like any method, it is not immune to errors. Ensuring accurate error detection is crucial for the reliability of survey results. So, how can surveyors achieve high precision in their work? Let’s delve into the techniques that can help detect and mitigate errors in compass surveying. Compass Surveying Techniques
Basics of Compass Surveying
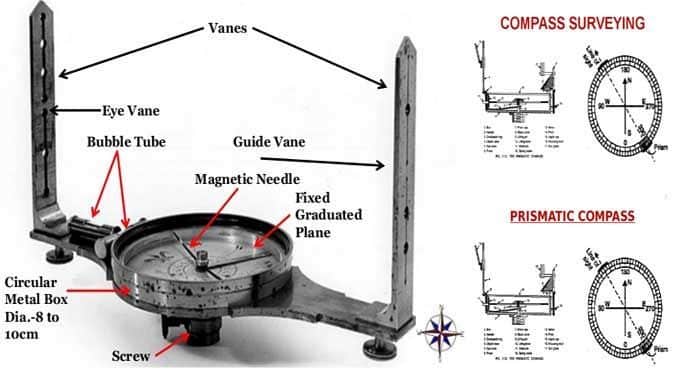
Components of a Surveying Compass
A typical surveying compass comprises several key components: the magnetic needle, the compass card, the sighting device, and the base plate. The magnetic needle aligns with the Earth’s magnetic field, pointing towards the magnetic north, while the compass card provides degree measurements. The sighting device helps in taking accurate bearings, and the base plate serves as the foundation for all these elements. Compass Surveying Techniques
How a Surveying Compass Works
A surveying compass operates by aligning its magnetic needle with the Earth’s magnetic field. Surveyors take bearings by sighting a target and reading the compass card’s degree measurement. This straightforward process makes compass surveying a preferred choice for many field tasks, though it requires careful handling to maintain accuracy.
Common Errors in Compass Surveying
Magnetic Declination
One of the most common errors in compass surveying arises from magnetic declination—the angle difference between true north and magnetic north. This error varies by location and changes over time, necessitating adjustments to maintain accuracy.
Instrumental Errors
Instrumental errors can occur due to imperfections in the compass itself, such as a bent needle or misaligned sighting device. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to minimize these issues.
Observational Errors
Human error is always a factor in manual surveying. Misreading the compass card, incorrect sighting, and poor recording can all contribute to inaccuracies.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors like nearby metallic objects, magnetic rocks, and even weather conditions can affect the compass needle’s behavior, leading to potential errors in measurements.
Techniques for Accurate Error Detection
Regular Calibration
Calibrating your surveying compass regularly is crucial. This involves comparing the compass readings with a known reference and making necessary adjustments to correct any deviations.
Adjusting for Magnetic Declination
Surveyors must account for magnetic declination by applying corrections based on current local declination values. This practice ensures that the bearings correspond accurately to true north.
Implementing Redundant Measurements
Taking multiple measurements of the same point and averaging the results can help identify and correct outliers, enhancing overall accuracy.
Using Check Lines
Check lines are additional lines surveyed to cross-verify the accuracy of main survey lines. If discrepancies are found, they can indicate potential errors in the primary measurements.
Advanced Error Detection Methods
Statistical Analysis
Using statistical methods to analyze survey data can reveal patterns and anomalies, helping to identify errors that may not be immediately apparent.
Software Tools
Modern surveying software offers tools for error detection and correction, providing automated analysis and adjustments to improve accuracy.
Cross-Verification with Other Surveying Methods
Combining compass surveying with other methods, such as GPS or total station surveying, allows for cross-verification. This approach helps identify and correct discrepancies between different datasets.
Practical Tips for Surveyors
Best Practices for Field Work
Always check your equipment before heading into the field.
Plan your survey route to minimize the impact of environmental factors.
Double-check your measurements and record data meticulously.
Handling Equipment
Handle your compass with care to avoid physical damage.
Store the compass in a stable, dry environment to prevent magnetization issues.
Recording and Analyzing Data
Keep detailed field notes, including conditions and any anomalies observed.
Use software tools for data analysis to identify potential errors quickly.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Successful Error Detection in Urban Surveying
In urban environments, where magnetic interference is prevalent, advanced techniques like cross-verification with GPS data have proven effective in maintaining high accuracy.
Overcoming Challenges in Rural Areas
Rural surveying often involves dealing with natural magnetic anomalies. Implementing redundant measurements and using check lines can help mitigate these challenges.
Innovative Techniques in Modern Surveying
Innovative methods, such as integrating drones for aerial surveying and using AI for data analysis, are pushing the boundaries of accuracy and efficiency in modern compass surveying.
Conclusion
Compass surveying remains a fundamental tool in the surveyor’s toolkit, but achieving high accuracy requires diligent error detection and correction. By employing techniques like regular calibration, adjusting for magnetic declination, and using advanced methods like statistical analysis and software tools, surveyors can significantly enhance the reliability of their results.
FAQs
What is the most common error in compass surveying?
The most common error in compass surveying is magnetic declination, which requires regular adjustments to ensure accuracy.
How often should I calibrate my surveying compass?
It’s advisable to calibrate your surveying compass before each major survey project or at least once every few months to maintain accuracy.
Can modern technology completely eliminate errors in compass surveying?
While modern technology can significantly reduce errors, it cannot completely eliminate them. Regular checks and a combination of techniques are still necessary.
What are the best tools for statistical analysis in surveying?
Software tools like MATLAB, Excel, and specialized surveying software can be very effective for statistical analysis.
How does environmental change affect compass surveying accuracy?
Environmental changes, such as the presence of magnetic rocks or nearby metallic objects, can influence the compass needle, leading to potential errors in measurements.