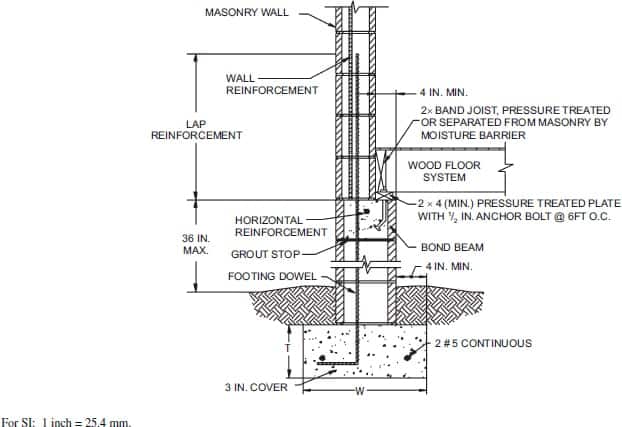
Masonry wall sections play a crucial role in the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of buildings. Ensuring compliance with building codes and standards is essential for safety, durability, and functionality. This comprehensive guide will delve into the critical aspects of masonry wall sections, emphasizing the importance of adhering to established building codes and standards.
Understanding Masonry Wall Sections
Masonry wall sections are composed of various materials such as brick, stone, concrete blocks, and mortar. These elements combine to create walls that are strong, fire-resistant, and energy-efficient. The key components of a masonry wall section include:
Facing Units: These are the visible parts of the wall, often made of brick, stone, or concrete blocks.
Backing Units: These support the facing units and can be made from similar or different materials.
Mortar: A mixture of cement, lime, sand, and water used to bond the units together.
Reinforcement: Steel bars or mesh embedded within the wall to enhance strength and stability.
Insulation: Materials added to improve thermal performance and energy efficiency.
Building Codes and Standards for Masonry Walls
Building codes and standards are designed to ensure the safety, durability, and performance of masonry walls. Some of the primary codes and standards governing masonry construction include:
International Building Code (IBC): Provides minimum requirements for building safety and structural integrity.
American Concrete Institute (ACI) Standards: ACI 530/530.1, also known as the Masonry Standards Joint Committee (MSJC) Code, sets guidelines for the design and construction of masonry structures.
ASTM International Standards: Various ASTM standards specify the properties and testing methods for masonry materials.
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Codes: Include requirements for fire resistance and safety in masonry construction.
International Building Code (IBC)
The IBC is a comprehensive set of regulations that provide minimum requirements for building safety, including masonry construction. Key aspects include:
Structural Design: Ensuring that masonry walls can withstand loads and stresses, including dead loads, live loads, wind loads, and seismic forces.
Fire Resistance: Specifications for fire-rated assemblies to protect building occupants and property.
Moisture Protection: Requirements for weatherproofing and moisture control to prevent water damage and deterioration.
Energy Efficiency: Guidelines for insulation and thermal performance to enhance energy conservation.
ACI 530/530.1 (MSJC) Code
The MSJC Code is a widely recognized standard for the design and construction of masonry structures. It addresses:
Material Specifications: Quality and properties of masonry units, mortar, grout, and reinforcement.
Design Procedures: Methods for calculating structural capacity, including load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls.
Construction Practices: Best practices for laying units, mixing and applying mortar, and installing reinforcement.
Inspection and Testing: Protocols for ensuring compliance with design specifications and identifying potential issues.
ASTM Standards
International provides numerous standards relevant to masonry construction, including:
ASTM C90:
Standard Specification for Loadbearing Concrete Masonry Units.
ASTM C270:
Standard Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry.
ASTM C476:
Standard Specification for Grout for Masonry.
ASTM C1314:
Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Masonry Prisms.
NFPA Codes
include specific requirements for fire safety in masonry construction, such as:
NFPA 221:
Standard for High Challenge Fire Walls, Fire Walls, and Fire Barrier Walls.
NFPA 5000: Building Construction and Safety Code, which includes provisions for fire-resistant construction.
Compliance Strategies for Masonry Wall Sections
Ensuring compliance with building codes and standards involves several critical strategies:
Design Phase
Engage Qualified Professionals: Collaborate with architects, engineers, and code experts to develop compliant designs.
Use Approved Materials: Select materials that meet or exceed the relevant ASTM standards and other specifications.
Detailed Drawings and Specifications: Provide comprehensive documentation to guide construction and facilitate code compliance.
Construction Phase
Qualified Workforce: Employ skilled masons and contractors with experience in masonry construction and knowledge of building codes.
Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control measures, including regular inspections and testing of materials and workmanship.
Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of construction processes, material tests, and inspections to demonstrate compliance.
Inspection and Testing
Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent inspections throughout the construction process to identify and address potential issues promptly.
Testing Protocols: Follow established testing protocols for materials and structural elements to ensure they meet specified standards.
Third-Party Verification: Consider using third-party inspectors and testing agencies for unbiased verification of compliance.
Benefits of Compliance
Adhering to building codes and standards for masonry wall sections offers numerous benefits:
Safety: Ensures the structural integrity and fire resistance of buildings, protecting occupants and property.
Durability: Enhances the longevity and performance of masonry walls, reducing maintenance and repair costs.
Energy Efficiency: Improves thermal performance, leading to lower energy consumption and costs.
Regulatory Approval: Facilitates obtaining necessary permits and approvals from building authorities.
Conclusion
Compliance with building codes and standards is essential for the successful construction of masonry wall sections. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, builders and designers can ensure the safety, durability, and performance of their masonry structures. From the design phase through construction and inspection, following best practices and utilizing high-quality materials are crucial steps toward achieving code compliance.